|
|
| Monitor page for changes |
by ChangeDetection |

|
|
|
||||||
 |
Clearly, I don't have the time or space to go through the steps
needed to use Winboard engines in every interface that supports it. Nor
do I have the time or space to go through the special quirks for each
each engine (that's what the whole site is for!). But for the
beginners, I will go through the set up the free Winboard and UCI chess
engine Yace. Yace is a german engine released by Dieter
Bürßner and together with Ruffian (WB/UCI), SOS 3 (UCI only)
,Crafty (WB and CB) is currently (March 2003) considered one of
the top free1 Winboard and UCI engines.
For some who are used only to chess playing programs like Chessmaster or Fritz, using Winboard engines is going to be a big culture shock.This is because Winboard compatiable interfaces generally (except for a few exceptions like Pondering) do not allow you to alter engine options within the interface itself. For example, if you have imported Yace into Winboard, and you wish to change the hash tables used in Yace, you will look in vain for an option that allows you to do that in the Winboard menus. Similarly if you wanted to turn the opening book off, you won't find it in the Winboard interface either.
The only way to accomplish this is to exit the program, then edit a setup file using a text editor. Unfortunately this might not be a straight forward matter either to a beginner, because there is no uniform naming convention for Winboard engines, so the setup file for one engine might be Yace.ini, while for another it might be Ruffian.cfg. If this isnt bad enough, the format itself of the setup file differs so one engine might require the line hash 40M to set the tranposition table size to 40 mb while another requires max_hashtb=40M to do the same.
Much of this results from the fact that Winboard engines are a diverse bunch with varying options and features. The Winboard protocol also is designed to be a loose interface, so it doesnt attempt to control the engines beyond the few necessary to run a chess match. The newer UCI has tried to address this problem to make setups within the interface more user-friendly.
If this does not scare you away, continue reading. The first part of this guide, teaches you how to figure out which file is the configuration file (yes it varies with each engine) and the common settings that are available. Once you have mastered this, the second part will cover the specific quirks of setting up in different winboard compatiable guis.
1) Go to http://home1.stofanet.dk/moq/download.htm
and download the latest Yace version.This happens to be the Paderborn
version (named after the tourney where Yace came in 2nd to Fritz).
2) Unzip the file and extract them to a directory. I, currently put all
my chess engines in a directory C:\engines. I create
a new folder for yace and unzip all the files into C:\engines\Yace
3) Before you import Yace into a Winboard compatiable interface, you
may want to configure Yace a little for your needs. For all Winboard
engines (not only Yace) , this involves looking for and editing the
configuration file2 The configuration file is almost always
a text file that you can edit in notepad. For Yace the configuration
file is named Yace.ini.
Steps 3 to 5 are not compulsory though, if you should
choose to go with the defaults. Altough tweaking the setups allows
you to get more out of the
engines.
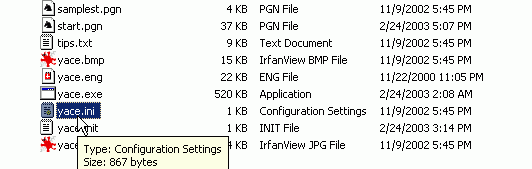
4) Be warned though, this does not mean that the setup file
for all Winboard engines end with the extension ini (or even have the
same format as you will see). For example, for crafty, the setup
file is named crafty.rc, in
ruffian it is ruffian.cfg. So
how do you know which is the setup file? Admittedly most of the time
it's obvious, files with the extension ini are most certainly the setup
files. Though occasionally you get a setup file with a unsual extension
like res. If you are not sure you can either read the readme files that
came with the program or refer to websites like WBEC (see below).
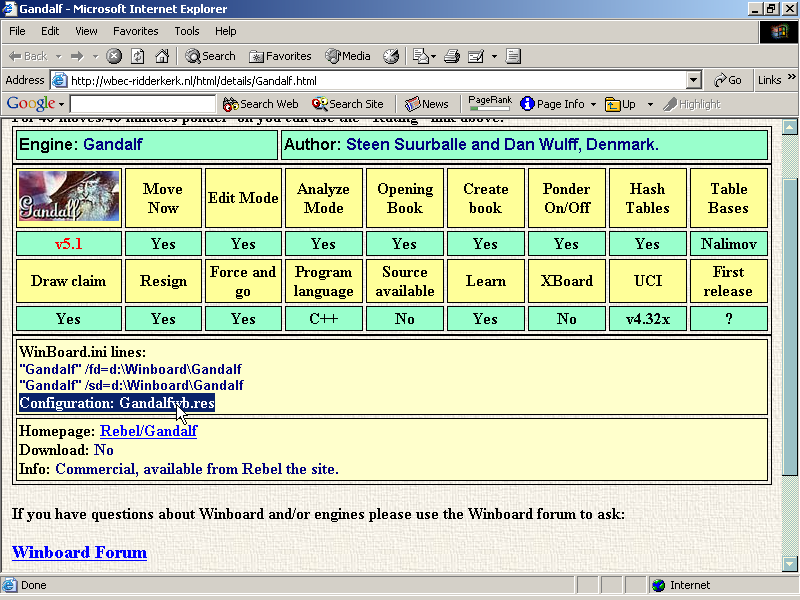
The WBEC site tells you about Gandalf
The following table, which is hardly exhaustive shows some common engines and the extensions of their configuration files.
| Chess engine | Extension of configuration file |
| Ametuer,Amyan,Anmon,Baron,Delfi,Dragon,King of Kings,Leila,Little Goliath,List,Pharaon,Smarthink,Terra,Wildcat,Yace | INI |
| Chezzz,Horizon,Kinightdreamer,Nejmet,Ruffian | CFG |
| Amy,Crafty,Quark,Sjeng | RC |
| Gromit,The Crazy Bishop | CUI |
| Gandalf,Tao | RES |
5. So let's start editing Yace.ini with your favourite text editor (Notepad works okay). Most of the defaults are okay for me, except I want Yace to use more memory for the transposition tables so I change the 8th line from the top to Hash 80M. Secondly, I edit the line that says tbldir to tbldir=c:\engines\egtb. This tells Yace that endgame tableabses can be found in that directory. If you do not have endgame tablebases, you can delete this line.You can see the final product below.
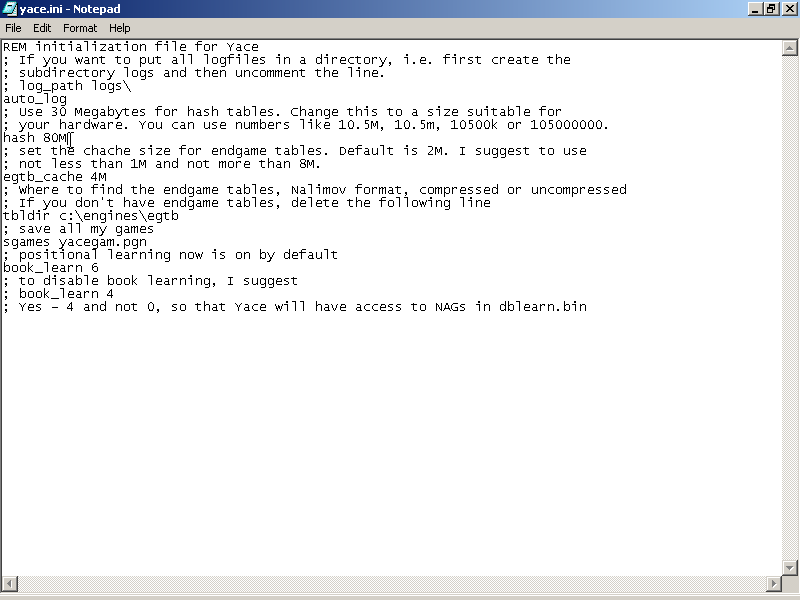
6. If you are wondering, how i knew what to edit, the answer is simple, I read the readme files that came with Yace. There are other configuration changes you can make of course, but in general for most engines, they involve one of the following
It's not possible unfortunately to give specific advice on how to alter the parimeters for each and every Winboard engine, since they do not all have the same features and all have different parimeter names even when refering to the same thing. For example, in Comet the line which controls the amount of memory to use in the transposition table is MAX_Hash, while in Yace as you have seen it is simply Hash. With some practice though, the main options (those mentioned above) becomes quite obvious, altough you still have to read the documentation that comes with the engine careful to look for obscure settings that might be avilable.
Almost all engines gives you the option of setting tranposition table sizes (commonly known as hash tables). For most engines the default tranposition size is set to a very low amount ,so as to not tax the older machines. So if you have more RAM, feel free to crank it up. Refer to my FAQ on transposition tables for more details on the optimal size.
By default, the chess engine does not know where the external endgame tablebases are being kept. Assuming you have some, for the engine to use them you have to specify the path to the directory where the endgame tablebases are. When it comes to opening books, most engines by default use opening books automatically as long as the opening book is in the same directory as the executable file. A few however include the provision for using opening books in other directories.
For most engines that have book or position learning options, there is usually a on/off switch to turn them on or off. Yace has a slightly for sophiscated version that uses different types of learning, refer to the doccumentation for more details
This sets whether the Winboard engine will resign. This can be useful to save time on playing out hopleless position. Most engines (Comet etc) have a simple on/off switch, others (Crafty,Yace) have a resign threshold you can set, beyond which the program considers the position hopeless and will resign.
Most engines are able to ponder. This means that when it is the opponent's turn to move, they will continue to analyze the position.However, in though pondering is one of the functions that can be set within the Winboard interface, some engines allow you to turn this on and off by editing the setup files .However this setting and be over-ridden within the interface.
Besides the options above, some Winboard engines (Crafty,Green light chess, Yace and more) allow you to change the style of play of engines, by altering the weights of positional factors (e.g value of pieces,passed pawns,open file etc) or by turning on or off certain extensions( R in null move, capture,check extensions) etc. As always your best guide is the documentation that comes with the engine.